by Amber Schroader, Paraben Corporation
When looking for new ways to expand your investigation business, the area of digital investigations can be very lucrative. Digital forensics, also known as digital investigations, serves as a crucial foundation in gathering and analyzing evidence for legal proceedings. Private Investigators can offer valuable services and key insights to a diverse range of clients.
Let’s start with exploring what digital forensics is. Digital forensics is a branch of forensic science encompassing the recovery, investigation, examination, and analysis of material found in digital devices, often in relation to mobile devices and computer crime. There are multiple areas of digital forensics that can be used in private investigations that will provide a wide range of options for clients.
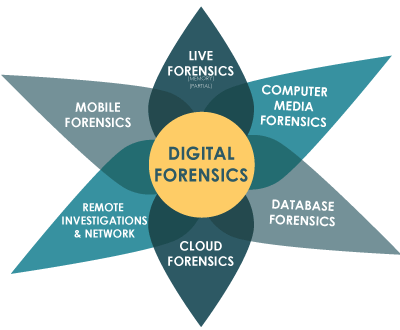
The different areas of digital investigations can provide a new profit center for your business (See Figure 1: Fields of Practice in Digital Forensics). Each specific field and specialization will require different skills, training, certification, and technology. Certain areas might be very appealing for private investigator clients. Examine the area of mobile forensics, for example. Mobile devices are common items associated with every individual and certainly play a role in every case.
Figure 1: Fields of Practice in Digital Forensics
When exploring new growth opportunities for your business, it’s important to weigh the costs of expansion against the potential benefits. One essential aspect of expanding into a new area is obtaining basic training. In digital forensics you need to learn the principles of the field to start with the proper foundation of knowledge. Online courses such as Digital Forensic Fundamentals are an excellent way to learn the basics. This vendor neutral course provides a comprehensive overview of the principles and perspectives of digital forensics (visit www.paraben.com/dfir-training-3/ to learn more).
Specialized Training
Once you have a foundational understanding of digital forensics as a whole, more specialized training in a particular field should be next. Again, focusing on the example of mobile forensics, there are a few areas where it can be used as a service on its own or as an add-on service in your practice.
Regarding mobile forensics training, often receiving it from the technology provider of the tool you select will benefit you the most. However, the training curriculum that is taught must be about foundational mobile forensic processes along with the use of the tool. Completing training that only shows how a tool works will cause you to miss out on the processes and details that take you from just clicking through buttons to understanding the data behind the buttons. Understanding the method behind the results allows you to offer a better overall service to your client.
(story continues below)

(story continues below)
Digital Forensic Tools
Examining the tools and technology used in the specialty you choose to expand into is vital. All technology in digital forensics is specialized to maintain the forensic principles of the data and produce the desired result. Pricing on technology can range from free, open-source options to mid-range tech with broad capabilities, to expensive options over $20,000. When dealing with digital evidence, it is essential to implement a cross-validation process, which is what makes digital forensics a branch of science. Cross-validation often requires purchasing more than one piece of technology. Open source options, such as a tool called Autopsy (Autopsy.com), are great options for a secondary tool, while your primary tool might be something on the commercial side, such as the E3 Forensic Platform (Paraben.com/digital-investigation-tools/). The more tools you have to use, the more options and services you can offer your clients.
Other Equipment
Other than the technology and training, you will also need other items to aid in the process of digital forensics. With mobile forensics, you will need the use of various Faraday technologies to ensure the devices are isolated from the network. With computer forensics, you need specific write protectors to protect the drive during the imaging process. The read-only requirements of computer forensics can cost more because of data storage and specialized equipment items. Another cost factor is the computer the technology is running on. One fundamental principle in digital forensics is that you cannot process potential evidence on the same machine you use for your general work. Investment in a machine dedicated to digital forensics doesn’t have to break the bank. Most of the technology providers will list the hardware recommendations for their tools. The best recommendation is a lot of RAM in the machine to make the process faster.
(story continues below)

(story continues)
After all the overhead is evaluated, it is time to look at what the return on your investment can potentially bring you. You should start by identifying your target market. As stated earlier, mobile devices are so prevalent that they are involved in many market opportunities. Many companies provide smartphones and tablets for their employees, but not every company has someone on staff to process those devices when the need arises. Another opportunity lies in partnering with local attorneys who may require digital forensics services for their clients. Additionally, the consumer market offers a steady demand for services such as malware and spyware processing and data recovery.
The potential for people to come to you for this specialized skill is almost endless. Figuring out the fee you are going to charge is very important. Many investigators choose to add these new offerings as an additional item in their hourly billing. There are arguments against this method as the different billing rates, one for normal work and one for specialized work, can get confusing to a customer. Instead, it can be beneficial to use flat-rate billing with an additional hourly rate after the flat rate time has ended. This approach can be budget-friendly to both parties and allow you to determine how many jobs must be completed to recover the overhead that was spent to start in the field. This type of billing can be done with both mobile forensics and computer forensics. Clients prefer to know upfront what to expect in terms of cost.
Digital forensics, as a field, has many different specialties and areas for expansion for private investigators. Most of these areas can yield a quick and easy return after a bit of training and time spent getting familiar with the field. Providing light-level services and relying on other firms with time in the field to do expert testimony can relieve some of the pressure that might have kept you out of this area of investigative services. As a natural investigator, incorporating some enhanced digital skills will produce a new profit center for your organization.
About the Author
Amber Schroader has been a driving force for innovation in digital forensics as the CEO of Paraben Corporation. Ms. Schroader has developed numerous software programs courses and guides in recovering data from smartphones, computer hard drives, cloud, email, and gaming systems. An accomplished design architect, curriculum developer, and instructor, Ms. Schroader has written and taught numerous classes for this specialized field and founded multiple certifications. Learn more about Ms. Schroader and Paraben at Paraben.com.






Good and informative.